Microelectronics world news
Research explores the effects of nuclear magnetic resonance on internal clock of cells
Wolfspeed quarterly revenue hit by weak industrial and energy markets
The Ripple Effects of Robert H. Dennard, Inventor of DRAM and Dennard Scaling
Cancel thermal airflow sensor PSRR with just two resistors

Self-heated transistors used as thermal air flow sensors are a particular (obsessive?) interest of mine, and over the years I must have designed dozens of variations on this theme. Figure 1 illustrates one such topology seen here before. It connects two transistors in a Darlington pair with Q2 serving as an unheated ambient thermometer and Q1 as the self-heated airflow sensor. Reference amplifier A1 and current sense resistor R3 regulate a constant 67 mA = heating current = 333 mW @ 5 V heating power.

Figure 1 Typical self-heated transistor thermal airflow sensor.
Wow the engineering world with your unique design: Design Ideas Submission Guide
This heat input raises Q1’s temperature above ambient by 64oC at 0 fpm air speed, cooling to 24oC at 1000 fpm as shown in Figure 2.

Figure 2 Thermal sensor temperature versus air speed.
As shown in Figure 2, the relationship between the airspeed and cooling of the self-heated transistor sensor is highly nonlinear. This is an inherent characteristic of such sensors and causes the sensor temperature versus air speed signal to be equally nonlinear. Consequently, even relatively small power supply instabilities, that translate % for % into instability in sensor temperature rise, can create surprisingly large airspeed measurement errors.
Clearly, anything less than perfect power supply stability can make this a problem.
But Figure 3 offers a surprisingly simple and inexpensive fix consisting of just two added resistors: R7 and R8.

Figure 3 Added R7 and R8 establish an instability-cancelling relationship between heating voltage V and heating current I.
The added Rs sum feedback from current sensing R3 with heating voltage source V. Summation happens in a ratio such that a percentage increase in V produces an equal and opposite percentage decrease in current I, and vice versa. The result is shown graphically in Figure 4.
Note the null (inflection) point at 5 V where heating is perfectly independent of voltage.

Figure 4: Sensor temperature versus supply voltage where: Blue = heating voltage V and (uncorrected) power; Red = heating current I; and Black = I*V = heating power / temperature.
Here’s the same thing in simple nullification math:
I = (0.2 – V*R8/R7)/R3 = (0.2 – 0.02V)/R3
H = I*V = (0.2V – 0.02V2)/R3
dH/dV = (0.2 – 0.04V)/R3 = (0.2 – 0.2)/R3 = 0 @ V = 5 volts
dH = -0.01% @ V = 5 volts ±1%
Note the 200:1 stability improvement that attenuates a ±1% variation in V down to only -0.01% variation in heating power and therefore temperature.
Problem solved. Cheaply!
Stephen Woodward’s relationship with EDN’s DI column goes back quite a long way. Over 100 submissions have been accepted since his first contribution back in 1974.
Related Content
- Self-heated Darlington transistor pair comprises new air flow sensor
- Nonlinearities of Darlington airflow sensor and VFC compensate each other
- Adding one resistor improves anemometer analog linearity to better than +/-0.5%
- Transistor linearly digitizes airflow
- A groovy apparatus for calibrating miniature high sensitivity anemometers
- 1kHz per Kelvin temperature sensor
The post Cancel thermal airflow sensor PSRR with just two resistors appeared first on EDN.
Is Rohm closer to acquiring Toshiba’s power chip business?

As Rohm Semiconductor deepens its ties with Toshiba Electronic Devices & Storage, industry watchers wonder if Rohm is getting closer to acquiring Toshiba’s power chips business. It all began late last year when the two companies announced a joint investment of $2.7 billion to collaborate on manufacturing power electronics devices.
But what made this news more noteworthy was that the announcement followed Rohm’s becoming part of a private equity group that was planning to take Toshiba private. However, when the two companies joined hands to boost the volume production of power devices, they stated that they had been considering this collaboration for some time and that it wasn’t a starting point in Rohm acquiring Toshiba’s power semiconductors business.
There is a third player in this $2.7 billion investment plan: the Japanese government, which adds another dimension to this hookup between Rohm and Toshiba Electronic Devices & Storage. Japan, aiming to strengthen the resilience of its semiconductor supply chains, recognises the strategic importance of power electronics and wants to double the power chip production in the country.
Moreover, Japan sees the local power chip industry as too fragmented, which makes it hard for them to compete with companies like Infineon. So, the Japanese government will subsidize one-third of this $2.7 billion investment in power semiconductor production on part of Rohm and Toshiba.
A closer look at this dimension also adds merits to the possibility of Rohm subsequently acquiring Toshiba’s power semiconductors business. It’s worth mentioning that Rohm was the first company to mass produce silicon carbide (SiC) MOSFETs, and it’s been continuously investing in this wideband gap (WBG) technology since then.

Figure 1 The Miyazaki Plant No. 2, based on assets acquired from Solar Frontier in July 2023, is dedicated to manufacturing SiC power devices. Source: Rohm
In the $2.7 billion joint investment plan announced late last year, Rohm will invest ¥289.2 billion in its new plant in Kunitomi, Miyazaki Prefecture, to produce SiC power chips. Toshiba will invest ¥99.1 billion in its newly built 300-mm fab in Nomi, Ishikawa Prefecture, to produce silicon-based power chips.
After delisting late last year, Toshiba faces an uncertain future. However, it still possesses highly valuable assets, and its power electronics business is one of them. There has also been chatter about splitting Toshiba into three units.

Figure 2 Vehicle electrification and automation of industrial equipment have led to strong demand for power devices like MOSFETs and IGBTs at 300-mm fab in Nomi. Source: Toshiba
When you see this potential divesture in the wake Japan’s desire to have a power electronics company that can compete with the likes of Infineon, Rohm taking over Toshiba’s power semiconductors business seems like a no-brainer. Among Japan’s current power chip firms, Rohm is known to have a stable power electronics business.
And the company is keen to affirm its management vision: “We focus on power and analog solutions and solve social problems by contributing to our customers’ needs for energy savings and miniaturization of their products.” Given this backdrop, Rohm taking over Toshiba Electronic Devices & Storage is probably a matter of time.
Related Content
- Toshiba is at crossroads, again
- New Rohm Fab Will Add Capacity for SiC Devices
- Zhenghai Group, Rohm Form JV for SiC Innovations
- Toshiba to spin off San Jose MPU engineering division
- Toshiba’s moment of semiconductor truth nears with upcoming split
The post Is Rohm closer to acquiring Toshiba’s power chip business? appeared first on EDN.
Waaree Renewable Technologies Limited Q4 results FY24
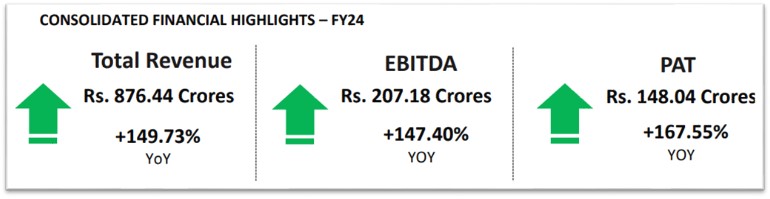
- Record Year of Strong Growth
- Record Revenue growth of 149.73% YoY at Rs. 876.44 crores and Record PAT growth of 167.55% YoY at Rs. 148.04 crores
- Unexecuted Orderbook of 2,365 MWp to be executed in next 18 months
Waaree Renewable Technologies Limited, the Solar EPC subsidiary of Waaree Group, a solar developer that finances, constructs, owns and operates solar projects, has reported its audited financial results for the quarter and nine month ended March 31, 2024.
KEY PERFORMANCE HIGHLIGHTSFY24
- Revenue for FY24 stood at Rs. 876.44 crores representing a growth of 149.73% YoY as compared to Rs.350.96 crores in FY23
- EBITDA for FY24 stood at Rs. 207.18 crores as compared to Rs. 83.75 crores in FY23 representing a growth of 147.40% YoY
- PAT for FY24 stood at Rs. 148.04 crores as compared to Rs. 55.33 crores in FY23 representing a growth of 167.55% YoY
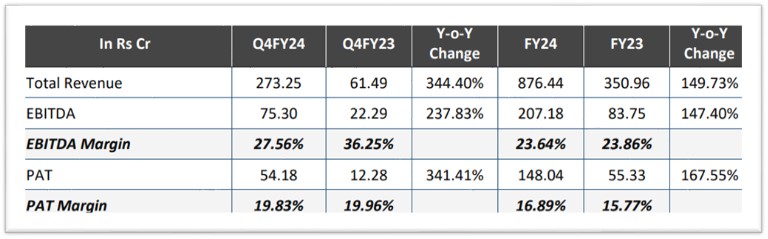
Q4FY24
- Revenue for Q4FY24 stood at Rs. 273.25 crores representing a growth of 344.40% YoY as compared to Rs. 61.49 crores in Q4FY23
- EBITDA for Q4FY24 stood at Rs. 75.30 crores as compared to Rs. 22.29 crores in Q4FY23 representing a growth of 237.83% YoY
- PAT for Q4FY24 stood at Rs. 54.18 crores as compared to Rs. 12.28 crores in Q4FY23 representing a growth of 341.41% YoY
Order book Position:
- Unexecuted order book stands at 2,365 MWp
- Bidding pipeline remains robust
Key Updates:
- The Company has successfully completed the corporate action of a stock split, reducing the face value of its Equity shares in the ratio of 1:5 per share. The face value of shares now stands at Rs. 2/- per share
- Recent Order Wins
- 980 MWp Ground Mounted solar power project
- 412 MWp Ground Mounted solar power project
- 450 MWp Ground Mounted Solar power Project
- 4 MWp Ground Mounted solar power project
Commenting on the results Mr. Dilip Panjwani, CFO, Waaree Renewable Technologies Limited said: “As a company committed to driving sustainable solutions, we are excited to share our progress and the significant opportunities that lie ahead. India has set an ambitious target to reduce the carbon intensity of the nation’s economy by less than 45% by the end of the decade, achieve 50 percent cumulative electric power installed by 2030 from renewables, and achieve net-zero carbon emissions by 2070. The country aims for 500 GW of renewable energy installed capacity by 2030.
The country’s renewable energy market is on the rise, with a record 69GW of bids in FY2024, surpassing the government’s target. Solar power, both grid-scale and rooftop, remains the primary contributor, accounting for 81% of the added capacity. The installed solar energy capacity has increased by 30 times in the last 9 years and stands at 81.81 GW as of March 2024.
Policy initiatives like the PM Surya Ghar: Muft Bijli Yojana aim to further boost solar installations, particularly in residential areas. With a strong balance sheet and disciplined financial management, the focus is on executing profitable projects with higher returns. This progress signifies not only environmental strides but also promising economic prospects in India’s renewable energy landscape.
We are also pleased to inform you that the board of directors has recommended a dividend of Rs. 1/- for the face value of share of Rs. 2/- each. With a sound balance sheet and disciplined capital management, we are well-equipped for the next phase of growth. We also would like to extend our gratitude to stakeholders for their continued trust and support.”
The post Waaree Renewable Technologies Limited Q4 results FY24 appeared first on ELE Times.
Key Concepts of Magnetic Materials
I built a WS2812 flower
 | My first attempt at something freeform. A couple of WS2812 controlled by a small esp32 board. The feet are connected to capacitive touch sensors to control on/off, color mode and brightness. [link] [comments] |
Broken UHF Radio
 | Ear piece no longer works on my radio after I went to the ground and landed on it causing the metal ring to come out. Radio still works fine just not with an ear piece. What would I have to do to go about fixing this? [link] [comments] |
Weekly discussion, complaint, and rant thread
Open to anything, including discussions, complaints, and rants.
Sub rules do not apply, so don't bother reporting incivility, off-topic, or spam.
Reddit-wide rules do apply.
To see the newest posts, sort the comments by "new" (instead of "best" or "top").
[link] [comments]
EEVblog 1614 - Circuit Design TIP: Crystal Oscillators
Microchip Preps Radiation Tolerant DC-DC Converters for Space
New MediaTek SoC Speeds Up Generative AI Processing at the Edge
CSconnected appoints Howard Rupprecht as new managing director
India Gears Up to Celebrate National Technology Day 2024
India celebrated its first National Technology Day on May 11, 1999, after the successful nuclear test at Pokhran in 1998, to commemorate the many achievements of the Indian scientific and technology fraternity. This day serves as a testament to India’s constant and relentless pursuit of excellence and innovation. It is an opportunity to celebrate and honor the collaborative efforts of scientists, engineers, entrepreneurs, and educators, towards building a better, more efficient, and supportive innovation ecosystem.
It goes without saying that behind every technological breakthrough are countless individuals and organizations working tirelessly to break the glass ceiling and achieve the unfathomable. Hence, National Technology Day reminds the Indian community to keep investing in research and development, further cementing a culture of science and innovation while ensuring equitable access to technology for all.
India’s Story in Building a Strategic Scientific and Technology ForumThe journey of technology and innovation has been nothing short of exceptional for India. The nation has been a treasure trove of knowledge from the very start of civilization. With a rich scientific heritage dating back thousands of years, India, to begin with, has made significant contributions including the concept of zero, the formulation of algebra and trigonometry, and the decimal system. Aryabhatta is considered to be a major early physicist and a mathematician who explicitly developed theories on the motion of planets.
Indian scientific community has made great advancements in the fields of medicine, astronomy, engineering, space, biotechnology, renewable energy, electronics, automotive, and defence. The government has put sincere efforts into establishing refined, top-notch, and highly competitive educational facilities like the Indian Institute of Technology (IITs) and Indian Institutes of Science (IISc) among others. Also, to bolster the R&D ecosystem in the country, institutions like the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR) and the Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO) have been established.
The Indian IT industry is booming to become a global hub with MNCs like Tata Consultancy Services, Wipro, and Infosys playing a crucial role in accelerating the nation’s economic growth. The Space program has achieved significant milestones, including the launch of satellites, lunar exploration missions (Chandrayaan-1 and Chandrayaan-2), and Mars exploration (Mangalyaan).
The story doesn’t end here; India is also among the top players in biotechnology and pharmaceuticals, with rapid development in areas like vaccine development, generic drug manufacturing, and biotech research. Also, the country is investing hugely in renewable energy stressing on adopting environment-friendly ways and technology in the long run.
How far has India Come?India in the last decade has seen major strides in the field of science and technology on a global level. Initiatives like “Make in India” launched by the GoI in 2014 aim at transforming the nation into a global manufacturing hub by attracting foreign investments, improving the ease of doing business, and promoting skill development, to revitalize the manufacturing sector and promote economic growth and job creation in the country. “Digital India” is another initiative launched with the vision of transforming India into a digitally-enabled and empowered society. It aims at leveraging digital technologies to bridge the digital divide and promote growth and development in varied sectors like electronics, automotive, IT, transportation, and communication.
With such initiatives being actively worked upon, India has been hit by the wave of startup culture. The EV sector is ramping up with denser infra being set up across the country. Technology leaders like Tesla and TATA are making their way in the EV segment in India. The country is boosting its semiconductor business with GoI investing bulk in setting up manufacturing units. We also saw mobile phone manufacturing jump 21 times to nearly Rs. 4.1 lakh Cr in the last 10 years.
Industry Speaks:Read with us what top thought leaders have to say as we observe National Technology Day this year.
Mr. Aalok Kumar, Corporate Officer & Sr. VP – Head of the Global Smart City Business at NEC Corporation and President & CEO at NEC Corporation India
“Over the past decade, India has matured into global leadership in technological innovation. This has altered how we experience how the day-to-day services are provided and above all, how citizens utilize civic services. This transformation is fundamentally underpinned by the recognition of technology’s potential to change lives and communities for the better. Today, India is on a steady path to realizing its vision for a ‘Viksit Bharat’ by 2047, and the role of technology comes into sharp focus with greater responsibility than ever before. At this juncture, the tech innovation ethos in India is evolving to “purposeful innovation” aimed at societal good, demanding creative and responsible application of AI, ML, and big data analytics to solve day-to-day problems of the common man.
At NEC India, our purpose is to build technology that serves the people, and as intelligent communities emerge, driven by data analytics and AI, we are proud to be playing our part in shaping a future where technology redefines citizen-centricity in civic services empowering lives. India’s unique position as a rapidly urbanizing nation undergoing large-scale digital transformation presents an unparalleled opportunity as a testing ground for innovative solutions that can be adapted to various markets worldwide.”
Mr. Sivakumar Selva Ganapathy, Vice President at OpenBlue India Software Engineering & APAC Solutions, Johnson Controls
“This year, India celebrates the 25th anniversary of National Technology Day. As we reflect on this journey, it is evident that our progress over the past two decades has been nothing short of remarkable. From our early achievements to emerging as a global technological hub today, India’s strength and capability in the domain speaks for itself.
While technology has impacted every sector in India, one area where it is poised to make a defining impact is sustainability. From building management systems analyzing occupancy patterns to AI-powered Smart grids optimizing energy distribution, technology is actively transforming cities into efficient and sustainable hubs. As a corollary, the area of green technology and green buildings is increasingly becoming more relevant, and as it continues to evolve, skilling & curriculum development assumes added importance. It is our firm belief that this can be best achieved through industry-academia collaboration.
At Johnson Controls India, we are observing a steady increase in the adoption of technologies for green buildings, and it won’t be long before buildings evolve from merely being smart, to autonomous – capable of governing and maintaining itself! This National Technology Day, as we look at the strides made, we also look forward to witnessing the future of green technologies unfold, and renew our commitment to innovating for a green tomorrow. “
The Way Forward for India India holds tremendous potential for innovation and collaboration in varied sectors including healthcare, education, transportation, and communication, where technology has permeated and unlocked new opportunities for growth and development.
India holds tremendous potential for innovation and collaboration in varied sectors including healthcare, education, transportation, and communication, where technology has permeated and unlocked new opportunities for growth and development.
National Technology Day is not merely about gadgets and gizmos but holds a more profound implication on how technology has impacted our society for the better. Technology has the power to democratize access to information, improve healthcare systems, enhance education, foster economic development, and promote sustainable development.
As we commemorate this day in 2024, let us look at the future with optimism and resolve and reaffirm our commitment to leverage the power of technology responsibly and ethically, to create a more inclusive and sustainable world.
The post India Gears Up to Celebrate National Technology Day 2024 appeared first on ELE Times.
How Wi-Fi sensing simplifies presence detection

The emerging technology of Wi-Fi sensing promises significant benefits for a variety of embedded and edge systems. Using only the radio signals already generated by Wi-Fi interfaces under normal operation, Wi-Fi sensing can theoretically enable an embedded device to detect the presence of humans, estimate their motion, approximate their location, and even sense gestures and subtle movements, such as breathing and heartbeats.
Smart home, entertainment, security, and safety systems can all benefit from this ability. For example, a small sensor in a car could detect the presence of back-seat passengers—soon to be a requirement in new passenger vehicles. It can even detect a child breathing under a blanket as it does not require line of sight. Or an inexpensive wireless monitor in a home could detect in a room or through walls when a person falls—a lifesaver in home-care situations.

Figure 1 Wi-Fi Sensing can be performed on any Wi-Fi-enabled device with the right balance of power consumption and processing performance. Source: Synaptics
Until recently, such sensing could only be done with a passive RF receiver relying on the processing capability of a nearby Wi-Fi access point. Now, it can be done on every Wi-Fi-enabled end device. This article explores how designers can get from theory to shipped product.
How it works
The elegance of Wi-Fi sensing is that it uses what’s already there: the RF signals that Wi-Fi devices use to communicate. In principle, a Wi-Fi receiving device could detect changes in those RF signals as it receives them and, from the changes, infer the presence, motion, and location of a human in the area around the receiver.
Early attempts to do this used the Wi-Fi interface’s receive signal strength indicator (RSSI), a number produced by the interface periodically to indicate the average received signal strength. In much the same way that a passive infrared motion detector interprets a change in IR intensity as motion near its sensor, these Wi-Fi sensors interpret a change in RSSI value as the appearance or motion of an object near the receiver.
For instance, a person could block the signal by stepping between the receiver and the access point’s transmitter, or a passing person could alter the multipath mix arriving at the receiver.
RSSI is unstable in the real world, even when no one is nearby. It can be challenging to separate the influences of noise, transmitter gain changes, and many other sources from the actual appearance of a person.
This has led researchers to move to a richer, more frequently updated, and more stable data stream. With the advent of multiple antennas and many subcarrier frequencies, transmitters and receivers need far more information than just RSSI to optimize antenna use and subcarrier allocation. Their solution is to take advantage of channel state information (CSI) in the 802.11n standard. This should be available from any compliant receiver, though the accuracy may vary.

Figure 2 Wi-Fi system-on-chips (SoCs) can analyze CSI for subtle changes in the channel through which the signal is propagating to detect presence, motion, and gestures. Source: Synaptics
CSI is reported by the receiver every time a subcarrier is activated. It is essentially a matrix of complex numbers, each element conveying magnitude and phase for one combination of transmit and receive antennas. A three-transmit-antenna, two-receive-antenna channel would be a 3 x 2 array. The receiver generates a new matrix for each subcarrier activation. So, in total, the receiver maintains a matrix for each active subcarrier.
The CSI captures far more information than the RSSI, including attenuation and phase shift for each path and frequency. In principle, all this data contains a wealth of information about the environment around the transmitter and receiver. In practice, technical papers have reported accurate inference of human test subjects’ presence, location, motion, and gestures by analyzing changes in the CSI.
Capturing presence data
Any compliant Wi-Fi interface should produce the CSI data stream. That part is easy. However, it is the job of the sensor system to process the data and make inferences from it. This process is generally divided into three stages, following the conventions developed for video image processing: data preparation, feature extraction, and classification.
The first challenge is data preparation. While the CSI is far more stable than the RSSI, it’s still noisy, mainly due to interference from nearby transmitters. The trick is to remove the noise without smoothing away the sometimes-subtle changes in magnitude or phase that the next stage will depend upon to extract features. But how to do this depends on the extraction algorithms and, ultimately, the classification algorithms and what is being sensed.
Some preparation algorithms may simply lump the CSI data into time bins, toss out outliers, and look for changes in amplitude. Others may attempt to extract and amplify elusive changes in phase relationships across the subcarriers. So, data preparation can be anything from a simple time-series filter to a demanding statistical algorithm.
Analysis and inference
The next stage in the pipeline will analyze the cleansed data streams to extract features. This process is analogous—up to a point—to feature extraction in vision processing. In practice, it is quite different. Vision processing may, for instance, use simple numerical calculations on pixels to identify edges and surfaces in an image and then infer that a surface surrounded by edges is an object.
But Wi-Fi sensors are not working with images. They are getting streams of magnitude and phase data that are not related in any obvious way to the shapes of objects in the room. Wi-Fi sensors must extract features that are not images of objects but are instead anomalies in the data streams that are both persistent and correlated enough to indicate a significant change in the environment.
As a result, the extraction algorithms will not simply manipulate pixels but will instead perform complex statistical analysis. The output of the extraction stage will be a simplified representation of the CSI data, showing only anomalies that the algorithms determine to be significant features of the data.
The final stage in the pipeline is classification. This is where the Wi-Fi sensor attempts to interpret the anomaly reported by the extraction stage. Interpretation may be a simple binary decision: is there a person in the room now? Is the person standing or sitting? Are they falling?
Or it may be a more quantitative evaluation: where is the person? What is their velocity vector? Or it may be an almost qualitative judgment: is the person making a recognizable gesture? Are they breathing?
The nature of the decision will determine the classification algorithm. Usually, there is no obvious, predictable connection between a person standing in the room and the resulting shift in CSI data. So, developers must collect actual CSI data from test cases and then construct statistical models or reference templates, often called fingerprints. The classifier can then use these models or templates to best match the feature from the extractor and the known situations.
Another approach is machine learning (ML). Developers can feed extracted features and correct classifications of those features into a support vector machine or a deep-learning network, training the model to classify the abstract patterns of features correctly. Recent papers have suggested that this may be the most powerful way forward for classification, with reported accuracies from 90 to 100% on some classification problems.
Wi-Fi sensing implementation
Implementing the front-end of an embedded Wi-Fi sensing device is straightforward. All that’s required is an 802.11n-compliant interface to provide accurate CSI data. The back-end is more challenging as it requires a trade-off between power consumption and capability.
For the data preparation stage, simple filtering may be within the range of a small CPU core. After all, a small matrix arrives only when a subcarrier is activated. But more sophisticated, statistical algorithms will call for a low-power DSP core. The statistical techniques for feature extraction are also likely to need the power and efficiency of the DSP.
Classification is another matter. All reported approaches are easily implemented in the cloud, but that is of little help for an isolated embedded sensor or even an edge device that must limit its upstream bandwidth to conserve energy.
Looking at the trajectory of algorithms, from fingerprint matching to hidden Markov models to support vector machines and deep-learning networks, the trend suggests that future systems will increasingly depend on low-power deep-learning inference accelerator cores. Thus, the Wi-Fi sensing system-on-chip (SoC) may well include a CPU, a DSP, and an inference accelerator.
However, as this architecture becomes more apparent, we see an irony. Wi-Fi sensing’s advantage over other sensing techniques is its elegant conceptual simplicity. But something else becomes clear as we unveil the true complexity of turning the twinkling shifts in CSI into accurate inferences.
Bringing a successful Wi-Fi sensing device to market will require a close partnership with an SoC developer with the right low-power IP, design experience, and intimate knowledge of the algorithms—present and emerging. Choosing a development partner may be one of the most important of the many decisions developers must make.
Ananda Roy is senior product line manager for wireless connectivity at Synaptics.
Related Content
- Going the Distance With Wi-Fi HaLow
- Exploring the superior capabilities of Wi-Fi 7 over Wi-Fi 6
- Paving the Way to Ambient-Powered Wireless Connectivity
- WIRELESS/RF: SenSiFi WiFi sensor module promises battery life of 3+ years
- Blocking 6-GHz Wi-Fi Is Costing Consumers Money and Quality Experiences
The post How Wi-Fi sensing simplifies presence detection appeared first on EDN.
ST’s 6-Axis Inertial Measurement Units Hit the Road
Handheld analyzers gain pulse generator option

FieldFox handheld RF analyzers from Keysight can now generate an array of pulse types at frequencies as high as 54 GHz. Outfitted with Option 357 pulse generator software, the FieldFox B- and C-Series analyzers give field engineers access to pulse generation capabilities that support analog modulations and user-defined pulse sequences. All that is needed to upgrade an existing analyzer is a software license key and firmware upgrade.

The software option includes standard pulses, FM chirps, FM triangles, AM pulses, and user-definable pulse sequences. In addition, it can create continuous wave (CW) signals with or without AM/FM modulations, including frequency shift keying (FSK) and binary phase shift keying (BPSK). Key parameters of the generated signal are displayed in both numerical and graphical formats.
FieldFox handheld analyzers equipped with pulse generation serve many purposes, including field radar testing for air traffic control, simulating automotive radar scenarios, performing field EMI leakage checks, and assessing propagation loss of mobile networks.
Find more datasheets on products like this one at Datasheets.com, searchable by category, part #, description, manufacturer, and more.
The post Handheld analyzers gain pulse generator option appeared first on EDN.
Software platform streamlines factory automation

Reducing shop-floor hardware, Siemens’ Simatic Automation Workstation delivers centralized software-defined factory automation and control. The system allows manufacturers to replace a hardware programmable logic controller (PLC), conventional human-machine interface (HMI), and edge device with a single software-based workstation.

Hundreds of PLCs can be found throughout plants, each one requiring extensive programming to keep it up-to-date, secure, and aligned with other PLCs in the manufacturing environment. In contrast, the Simatic Workstation can be viewed and managed from a central point. Since programming, updates, and patches can be deployed to the entire fleet in parallel, the shop floor remains in synch.
Simatic Workstation is an on-premise operational technology (OT) platform. It offers high data throughput and low latency, essential for running various modular applications. Simatic caters to conventional automation tasks, like motion control and sequencing, as well as advanced automation operations that incorporate artificial intelligence.
The Simatic Automation Workstation is the latest addition to Siemens’ Xcelerator digital business platform. Co-creator Ford Motor Company will be the first customer to deploy and scale these workstations across its manufacturing operations.
Find more datasheets on products like this one at Datasheets.com, searchable by category, part #, description, manufacturer, and more.
The post Software platform streamlines factory automation appeared first on EDN.
Silicon capacitor boasts ultra-low ESL

Joining Empower’s family of E-CAP silicon capacitors for high-frequency decoupling is the EC1005P, a device with an equivalent series inductance (ESL) of just 1 picohenry (pH). The EC1005P offers a capacitance of 16.6 µF, along with low impedance up to 1 GHz. A very thin profile allows the capacitor to be embedded into the substrate or interposer of any SoC, especially those used in high-performance computing (HPC) and artificial intelligence (AI) applications.

E-CAP high-density silicon capacitor technology fulfills the ‘last inch’ decoupling gap from the voltage regulators to the SoC supply pins. This approach integrates multiple discrete components into a single monolithic device with a much smaller footprint and component count than solutions based on conventional multilayer ceramic capacitors.
In addition to sub-1-pH ESL, the EC1005P provides sub-3-mΩ equivalent series resistance (ESR). The capacitor comes in a 3.643×3.036-mm, 120-pad chip-scale package. Its standard profile of 784 µm can be customized for various height requirements.
The EC1005P E-CAP is sampling now, with volume production expected in Q4 2024. A datasheet for the EC1005P was not available at the time of this announcement. For more information about Empower’s ECAP product family, click here.
Find more datasheets on products like this one at Datasheets.com, searchable by category, part #, description, manufacturer, and more.
The post Silicon capacitor boasts ultra-low ESL appeared first on EDN.